When it comes to gardening, it’s essential to understand that not all soils are created equal. While it might seem as if you could simply scoop up some earth from your backyard and use it to pot your houseplants, the reality is much different. Garden soil and potting soil have unique properties that make them suitable for different uses. In this article, we will dig deep into the differences between garden soil and potting soil, how to use them appropriately, and tips for selecting the best soil for your plants.
What is Garden Soil?
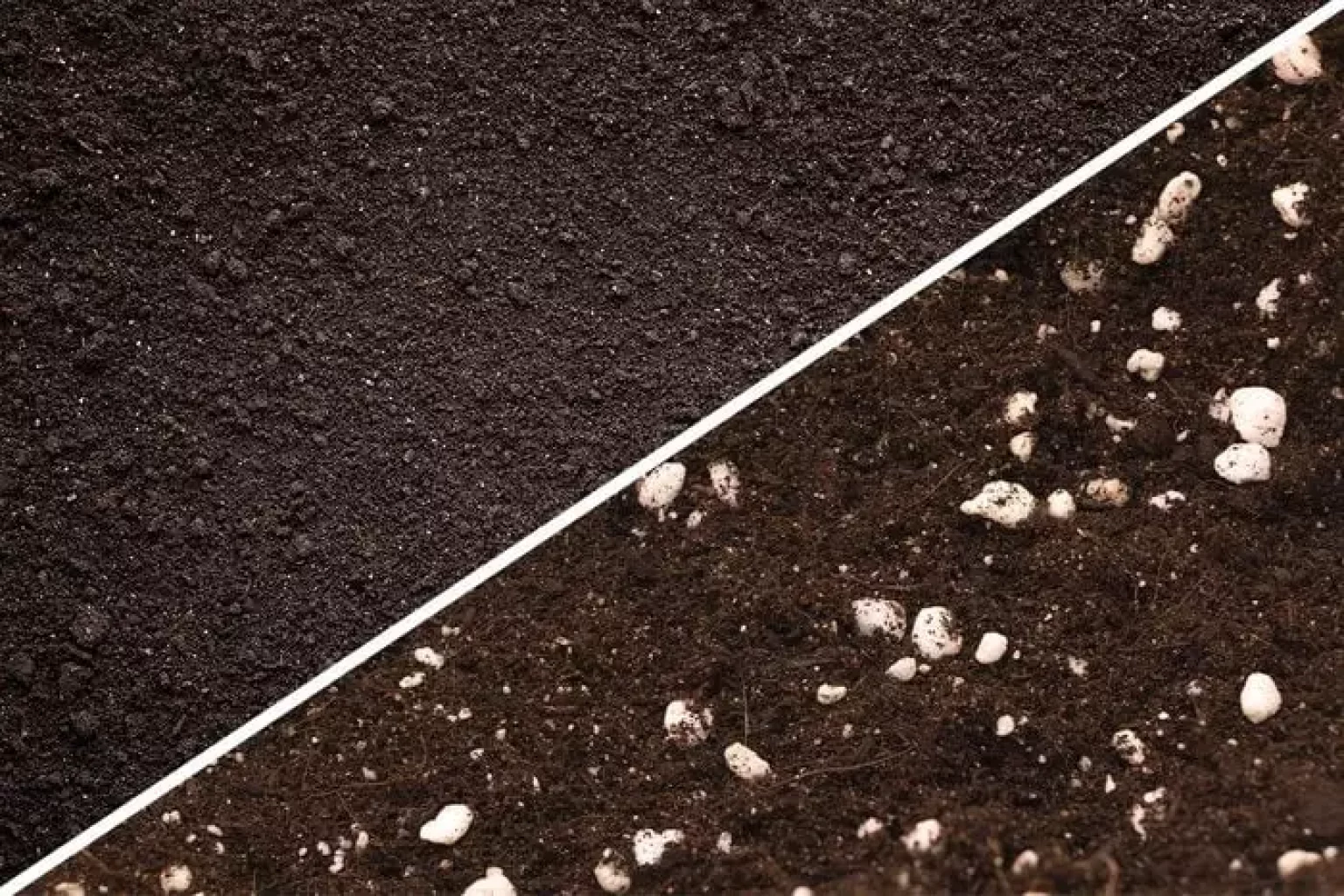
Garden soil, often called topsoil or native soil, is the layer of soil that exists in your garden. It’s a complex ecosystem filled with nutrients, minerals, organisms, and decaying organic matter that gives life to your plants. Garden soil varies greatly from place to place due to local climate, geology, and vegetation.

Pros and Cons of Garden Soil
- Pros: Garden soil is rich in minerals and organic matter, making it a perfect medium for plants to grow in the garden. It can retain moisture well, which is beneficial for most plants. Plus, it’s cost-effective and readily available in your yard.
- Cons: On the flip side, garden soil is dense and can compact easily, restricting root growth. It may contain weed seeds, pests, or disease organisms that could harm your plants. Its nutrient content can vary, and it’s not ideal for container gardening due to poor drainage.
What is Potting Soil?
Potting soil, also known as potting mix, is a blend of various organic and inorganic materials that are designed to provide optimal growing conditions for potted plants. Unlike garden soil, it’s sterilized to eliminate disease and weed seeds and is lighter and more porous to ensure good drainage.

Pros and Cons of Potting Soil
- Pros: Potting soil is sterile, lightweight, and drains well, preventing waterlogged roots. It’s designed for container plants, providing a stable environment for root growth. Many potting soils are also fortified with slow-release fertilizers.
- Cons: Potting soil is typically more expensive than garden soil and may require supplemental fertilizing over time. It may also dry out faster, requiring more frequent watering.
Garden Soil vs. Potting Soil: The Major Differences

In comparing garden soil vs. potting soil, the primary differences boil down to their composition, drainage, nutrient content, and intended use.
- Composition: Garden soil is composed of clay, sand, and silt, with varying amounts of organic matter. Potting soil, on the other hand, contains ingredients like peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite, which help to retain moisture and create air pockets for roots to breathe.
- Drainage: While garden soil retains water well, it can become overly compacted and waterlogged in containers. Potting soil is specifically designed to drain well, preventing root rot in potted plants.
- Nutrient Content: Garden soil contains naturally occurring nutrients, while potting soil often includes added nutrients and fertilizers, tailored to the needs of container plants.
- Intended Use: Garden soil is best used for in-ground gardening, while potting soil is ideal for container plants.
Choosing the Right Soil for Your Plants

Understanding your plants’ needs and the differences between garden soil vs. potting soil will help you make the best choice. As a rule of thumb, use garden soil for planting in your garden and potting soil for indoor plants and container gardening.
Select soil that meets the specific requirements of your plants in terms of pH, nutrients, and moisture retention. For instance, succulents prefer well-draining soil with less organic matter, while ferns thrive in a rich, moisture-retaining mix.
Conclusion
In the end, the choice between garden soil and potting soil depends on your specific needs. Both types have their roles in gardening, and understanding their unique characteristics is key to a flourishing garden. Whether you’re planting a lush outdoor vegetable garden or nurturing a delicate orchid indoors, choosing the right soil is the first step towards a thriving plant.